A 403 Forbidden Error means your website or a specific page is blocking visitors from viewing it. When someone tries to visit your page, the server refuses to let them in. Instead of loading the page, it shows the 403 error message.
This error is a big deal because it keeps visitors out, which can hurt your site’s trust and user experience. If people can’t reach your content, they’ll leave and may not come back. Search engines may also notice, which can affect your site’s search rankings.
Fixing a 403 error is important to keep your site running smoothly and make sure people—and search engines—can see everything they’re supposed to.
Quick Links
What Is a 403 Forbidden Error?
A 403 Forbidden Error is part of a group of messages called HTTP status codes. These codes tell us how a request between a browser and a website is going. A 403 means the request went through, but access is not allowed.
This error usually pops up when the server understands the request but refuses to let it happen. It’s like someone ringing your doorbell, but you’ve locked the door and decided not to answer.
There are many reasons why this might happen. It could be that permissions are set too tightly, or that your site is blocking certain users or files by mistake.
Common Causes of a 403 Forbidden Error
Wrong file permissions can stop your site from showing files. Each file and folder on your website has permission settings. If these aren’t set right, your server may block access.
A broken or badly edited .htaccess file can also be the reason. This file controls how parts of your site work. If there’s a mistake in it, your server might start blocking users.
Plugins or themes on WordPress can sometimes mess with permissions or create security conflicts. A new update or a bad plugin can suddenly trigger this error.
IP blocking, server ownership errors, or bad server settings on Apache or NGINX can also cause the 403 message. Even something like a missing folder owner can break access.
How to Fix a 403 Forbidden Error (Platform-Specific Solutions)
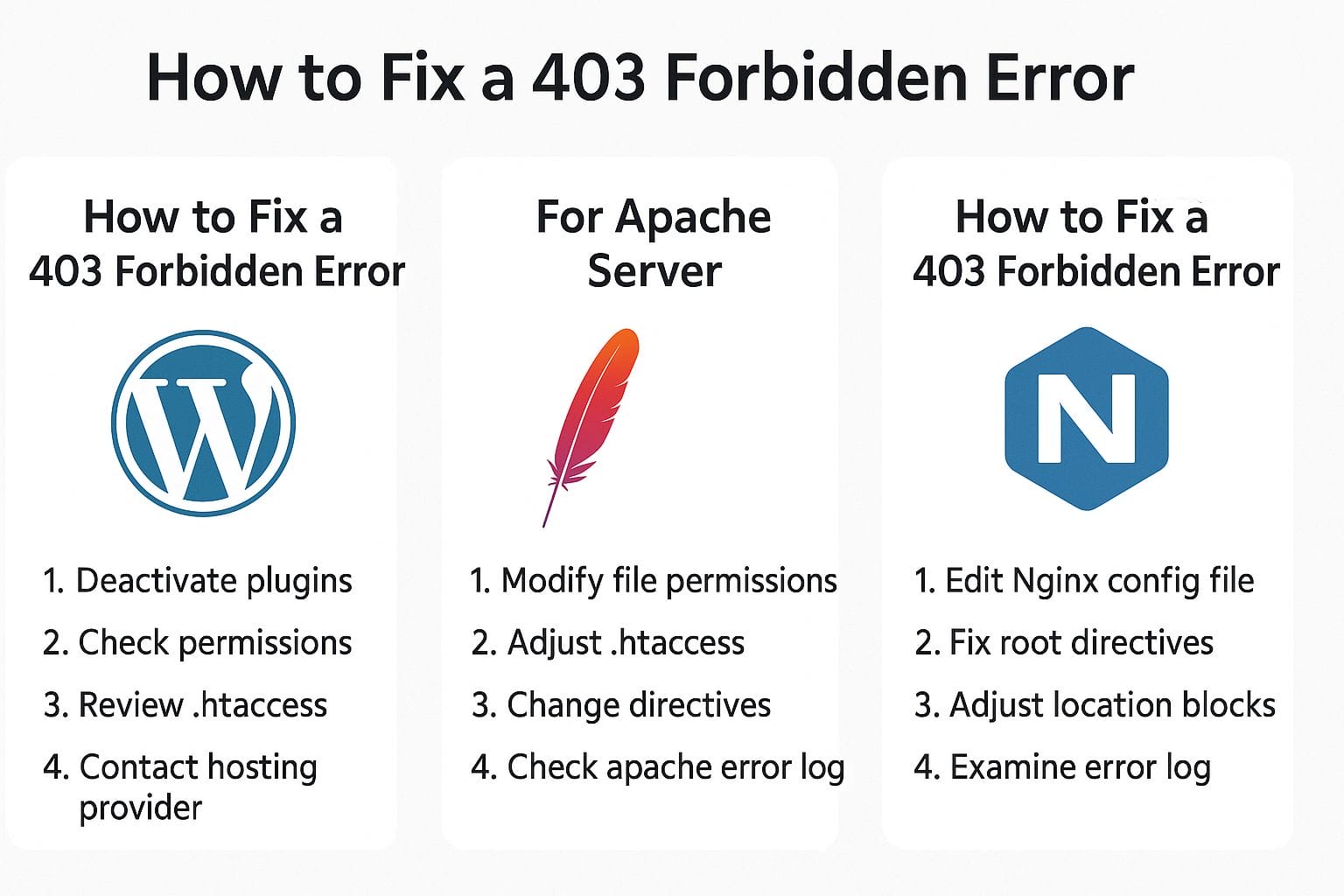
1. For WordPress Sites
Start by turning off plugins one by one. A plugin might be blocking access without you knowing. Turn off each one and check if the error disappears.
Next, try regenerating your .htaccess file. You can delete the old one and let WordPress make a fresh one by going to your permalink settings and hitting save.
Also, check your file and folder permissions. WordPress needs certain settings to work. Folders should be 755, and files should be 644. Anything stricter might cause problems.
2. For Apache Server
Make sure permissions on files and folders are correct. Use CHMOD to set them properly—folders should be 755 and files 644.
Look inside your .htaccess file for any rules that may be blocking access. Even one wrong line can cause trouble.
Check your Apache config files to make sure they’re not rejecting users or folders by accident. You may need root access to do this.
3. For NGINX Server
Check your NGINX settings to see if directory access is blocked. Make sure directory indexing is allowed if needed.
Review your server block permissions to make sure your site’s root folder is readable by the server.
Look at “deny” and “allow” rules. NGINX can block IPs or entire folders this way, so check for those lines in your config files.
4. Using cPanel
Use File Manager in cPanel to check and change permissions on folders and files. Make sure nothing is set to “000” or other restricted values.
Check IP Blocker in cPanel to make sure your own IP or your users’ IPs haven’t been blocked by mistake.
Visit Directory Privacy to make sure folders aren’t locked behind passwords or permission settings that are too strict.
Tools to Help Diagnose 403 Errors
Google Search Console can alert you if search engines are seeing errors on your pages. It’s a good first place to check.
Server logs (like access logs or error logs) show what the server tried to do when the error happened. Look there for clues.
There are also online tools that show HTTP status codes. These can help you check if the error is happening globally or just for you.
If you use a hosting control panel, it might have built-in tools to scan permissions, plugin conflicts, or .htaccess problems.
How to Prevent 403 Errors in the Future
Keep your themes and plugins updated. Updates often fix bugs that could lead to errors like this.
Backup your .htaccess file regularly, especially if you change settings often. That way, you can restore a working version fast.
Use the principle of least privilege when setting permissions. Only give as much access as needed. This lowers the chance of something being blocked by mistake.
Be careful with security plugins—they can block access too tightly. Test changes before applying them to your whole site.
Set up firewall rules the right way. A bad rule can lock out users or even block your whole site.
When to Contact Your Hosting Provider
If you’ve tried everything and the error still shows up, it might be a server-wide issue. That’s something only your host can fix.
Sometimes you can’t reach the files or folders you need. If that’s the case, and you don’t have access to settings, your host can help.
Your host might also need to fix a misconfiguration on their end—something you can’t see or touch as a regular user.
Why does the 403 error still show even after fixing permissions?
There could be another cause—like a plugin or server config—that’s still blocking access. It’s not always just about file permissions.
Can Cloudflare cause a 403 forbidden error?
Yes, if Cloudflare is set to block certain IPs or users, it can lead to this error. Check your Cloudflare firewall rules and settings.
What’s the difference between 403 and 401 errors?
A 401 error means you need to log in or give credentials. A 403 means you’re not allowed in—even with login details. It’s a straight denial.
Final Thoughts
A 403 error can seem scary, but it’s often caused by something small like a bad setting or permission. Fixing it quickly helps keep your website working and available to everyone.
It’s a good idea to check your site regularly for errors and run updates to prevent these problems in the future. A healthy website means happy users and better search rankings.
Interesting Reads:
Steps to Build a Keyword Strategy That Actually Works
How AI Search Platforms Are Evolving with NLP and Personalization?
SEO vs SEM: Which One Wins for Traffic Conversions and Brand Awareness?



