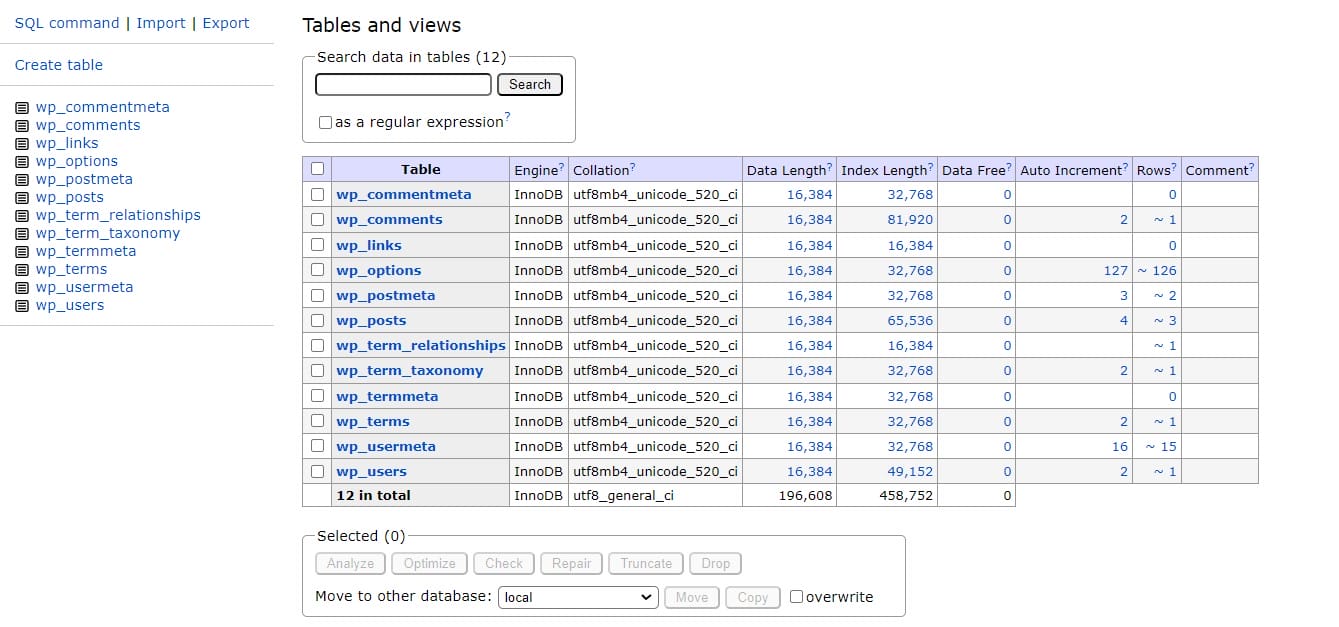
When setting up a WordPress site, a robust and well-organized database is essential for managing content, user interactions, and site settings. WordPress, a popular content management system (CMS), uses a set of default database tables to store and organize data. Each table has a specific role, contributing to the overall functionality of the website. In this post, we’ll explore the default WordPress database tables, what they do, and how they work together to power your site.
Quick Links
Default WordPress Database Tables
Upon installing WordPress, several tables are created in the database. Each table plays a crucial role in managing different aspects of your site.
1. wp_posts
-
- Purpose: Stores all content related to posts, pages, and custom post types.
- Details: Includes data such as post titles, content, status (published, draft), and post type (post, page, attachment, etc.).
2. wp_postmeta
-
- Purpose: Stores metadata for posts, pages, and custom post types.
- Details: Allows you to store additional information about posts, such as custom fields and plugin-specific data.
3. wp_terms
-
- Purpose: Manages taxonomy terms like categories and tags.
- Details: Contains the names of terms used in taxonomies.
4. wp_term_taxonomy
-
- Purpose: Defines the taxonomy and the relationship between terms and taxonomies.
- Details: Links terms to a specific taxonomy (e.g., categories or tags) and includes additional taxonomy data.
5. wp_term_relationships
-
- Purpose: Manages the relationship between posts and terms.
- Details: Associates posts with terms in various taxonomies (e.g., which posts belong to which categories).
6. wp_usermeta
-
- Purpose: Stores metadata about users.
- Details: Includes information such as user preferences, roles, and additional profile data.
7. wp_users
-
- Purpose: Contains user account information.
- Details: Stores usernames, passwords (encrypted), email addresses, and other user-related details.
8. wp_options
-
- Purpose: Holds site-wide settings and options.
- Details: Includes configuration settings such as site URL, admin email, active plugins, and theme settings.
9. wp_comments
-
- Purpose: Manages comments on posts and pages.
- Details: Stores comment content, author, email, and associated post ID.
10. wp_commentmeta
-
- Purpose: Stores metadata related to comments.
- Details: Allows additional information to be attached to comments.
11. wp_links
-
- Purpose: Manages blogroll links (links to other websites).
- Details: Used for managing external links; this table is often unused in modern WordPress installations as the Blogroll feature is deprecated.
12. wp_termmeta (introduced in WordPress 4.4)
-
- Purpose: Stores metadata for terms.
- Details: Allows additional data to be stored for taxonomy terms.
How These Tables Work Together
Each table in the WordPress database plays a unique role, but they all work together to ensure the smooth operation of your site. For instance:
- Content Management: wp_posts and wp_postmeta manage and store the core content, while wp_terms, wp_term_taxonomy, and wp_term_relationships handle content categorization.
- User Management: wp_users and wp_usermeta keep track of user information and settings.
- Site Settings: wp_options stores configuration settings crucial for site management.
- Comments and Interactions: wp_comments and wp_commentmeta manage user feedback on content.
Understanding the default WordPress database tables is crucial for managing and troubleshooting your WordPress site effectively. Each table has a specific role, contributing to the overall functionality of the website. By familiarizing yourself with these tables, you gain insight into how WordPress organizes and retrieves data, which can help you optimize, troubleshoot, and customize your site to better meet your needs.
Interesting Reads:
How To Convert A WordPress Site To A Static HTML Website
WordPress Attachment To Custom Post Type Does Not Have Parent